
The overall objective of this section is to further understand what is involved in PE subject leadership and to be able to construct strategies to improve PE in a primary school.
The following elements will be covered:
- Introduction to PE subject leadership.
- Pupils' progress and attainment.
- Observation of pupil performance.
- Progression in PE and attitudes within PE.
- Construct and monitor strategies to improve the overall quality and attainment within PE
Reflective TaskDiscuss:
There are 16 actions that a subject leader may need to undertake (or possibly delegate). Read through and reflect on each statement. Are they the job of the PE subject lead? Are there any that you would add?
|

1.Role.
You might have a job title which might include: Subject Leader, subject coordinator, physical education lead etc. Essentially this is the name for their job role. A job role is the expected function of that person. If they are a subject leader then the role is for them to lead with the expected pattern of behaviour that the work lead would suggest.
2.Responsibility.
Responsibilities are the specific tasks or duties that the role entails and which the post holder would be expected to complete as a function of their role. They are the specific activities or contractual obligations for which the subject leader is held accountable. Specific responsibilities are usually listed in job descriptions.
Candidates should be clear about what their role and responsibilities entail and this should include leading sustainable development - a key feature of effective leadership in any organisational context. A slight issue might arise here if a candidate has the job title ‘coordinator’ and their role and responsibilities do not include leadership!
Tutors can begin to ask questions that challenge and develops a candidates understanding of their role and responsibilities. “What is the difference between a role and a responsibility?” “Are all of your roles / responsibilities the same?” “How do they differ?” “Do you carry out other duties outside of your role and responsibilities?”
3.The priority list
i. Shaping a vision for the strategic direction of physical education that promotes success for all pupils e.g.
- keeping up to date with school, local and national initiatives to form a strategic view of physical education improvement within the whole school context
- developing a vision for PE
- creating, a subject development/action/strategic plan based on rigorous self-evaluation including manageable targets for sustainable improvement
- producing a handbook for PE that complements whole school publications with appropriate policies and information to ensure smooth running of the subject on a day to day basis
ii. Leading and managing effective planning, teaching, learning and assessment
e.g.
- leading the development of a scheme of work for PE and units of work
- leading the collection of assessment information to form a judgement about the quality of learning and teaching across the department
- grow excellent, evidence-based teaching
- agree targets for improvement in teaching and learning
- monitoring progress against subject and school targets
- analysing assessment information to evolve curriculum provision and develop teaching
- initiating intervention when required to keep staff and pupils on track
- evaluating the effectiveness of school and departmental plans and policies
- creating a challenging, supportive and progressive climate for learning in and through physical education
iii. Leading and managing staff e.g.
- ensuring that there are clear lines of communication between the staff, parents, pupils, other subjects and senior leaders
- supporting teachers with implementation of rewards and sanctions for pupils in PE
- managing effective training for all teachers of PE including peer, formal and informal observation and encouraging continuing professional development
- co-ordinating performance management for staff
- carrying out regular lesson observations - formal and informal, work sampling exercises, learning walks and feeding back to individuals and senior leaders as appropriate
iv. Development and deployment of staff and resources e.g.
- sharing information about resources that are available for teaching PE including strategies and content from other subject areas
- advising senior staff about the individual teachers and their level of expertise and specialisms
- ensuring all staff, including pupils and visitors understand and follow school policies and procedures including those related to safeguarding and health and safety
- managing the allocated budget for the subject area and seeking opportunities to fund aspects of the subject development plan
3.Summarising the role / objective of a subject leader:
This should be written and read something like…
“To provide professional leadership and management for physical education to secure high quality curriculum, teaching, and assessment and effective use of resources which leads to improved progress, attainment and behaviour (improved standards of learning) for all pupils, including those who are disadvantaged or have particular needs (for example, Pupil Premium, SEND, EAL or the most able pupils).”
Reflective TaskDeveloping a ‘futures’ vision for PE1.List words that portray your values in education (are these aligned to the school values?). 2.Use these words to write a short paragraph about your ‘futures’ vision for PE in your school in 5+ years time |
1.Values: What are candidate’s values? Values are important because they are influential in our thoughts, words and actions. Decisions we make are a reflection of our values and beliefs. Our values are important because they help us to grow and develop. If the values of a school or subject are agreed and common, then they can be very powerful in shaping our direction towards a specific purpose.
2.Futures Vision. Consider your own values, some informed thinking and imagination to envisage what ‘the future’ might look like for physical education practice in 5+ years time. It is important to develop a vision which focuses the direction of any strategy we implement.
Imagining practice in 5-10 years time is often called ‘Futures Vision’. If teachers have already developed a vision for physical education, then they should be encouraged to bring it to the session with them. This vision will of course be aligned to your role and responsibilities.
3.Medium-term strategy. Many school leaders and middle leaders develop a medium-term strategy which is usually 3-5 years.
The medium-term strategy should provide strategic actions progressive towards achieving the futures vision.
4.Operational planning. This is often termed a short-term strategy, a strategic plan, a development plan or an action plan. It outlines the detail or the strategy and actions that will be implemented.
The duration of the strategy design, implementation and evaluation might be anything between 12-24 months. For the majority of schools it will almost certainly be on an annual basis. Operational planning should result in listing all of the actions, measures and impact expected over 1-2 years and should be progressive to achieving medium term strategic goals.
5.Ofsted (2016) currently inspect whether leaders revisit their vision on a ‘regular’ basis. This is good leadership practice. Information is not provided as to how often ‘regular’ is, but assuming it was every 2-3 years, the vision will continuously be ‘moved’ and previous ‘futures vision’ will evolve into a medium-term strategy (see task in point 2 above).
Futures vison by definition, therefore is realised at the operational planning stage.
What is important to understand is that any operational planning or short-term strategy starts with the vision in mind.
To establish the start point it is important to conduct an audit.
Reflective ActivityLearner activity: 1.What is the difference between leadership and management? 2.Organise the word list into two appropriate columns |
Primary PE leaders have a vital role in sustaining and developing all pupils' PE learning experiences and achievements and raising standards for all. Senior leaders, need and expect all middle leaders to be engaged in whole-school development.
The most effective schools have leadership that stretches beyond the senior team and includes various levels of leadership within the school, Ofsted have said, of subject areas where practice is effective:
- There is a systematic approach to the monitoring of teaching and learning and of progress in implementing action plans.
- Subject leaders evaluate regularly and pupil progress data is routinely analysed.
- There are clear lines of accountability and the structures for performance management are known, understood and implemented.
- Head teachers support subject leaders with planning, training and observation.
- Analysis of pupils' performance has improved and targets are set for individual pupils, validated against previous results.
- Underperformance is tackled promptly and rigorously.
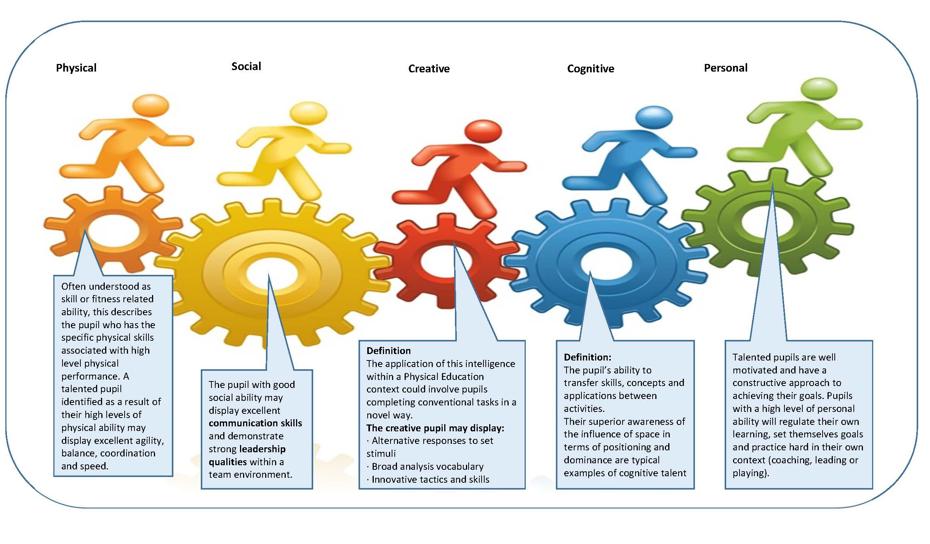
PE’s contribution to learners' personal development
PE is not just about knowledge, skills and understanding about activities, sports and performance. Children learn a great deal more from their physical education lessons, including personal and social skills, ability to take turns, and work in teams, the strength of character to win and loose and to cope with both, to persevere when things get tough and to stick at things that don't always come easily. Most importantly physical education contributes to a child's awareness of active life styles and the decisions they make on a daily basis to take activity for health benefits.
Reflective TaskAsk yourself...
|
Reflective ActivityConsider the following questions
|
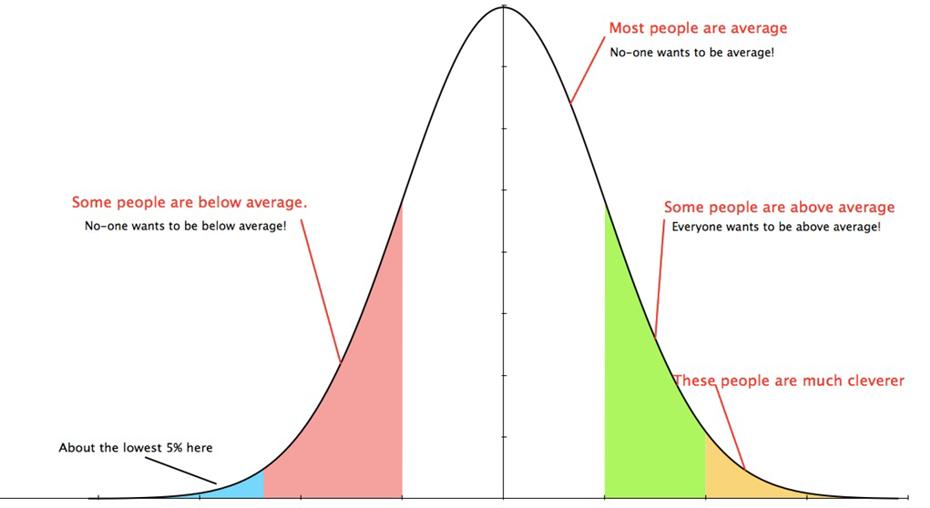
Distribution Curves
A normal distribution, sometimes called the bell curve, is a distribution that occurs naturally in many situations. For example, the bell curve is seen in tests like the SAT and GRE. The bulk of students will score the average , while smaller numbers of students will score above or below average or D. An even smaller percentage of students score an well above or well below. This creates a distribution that resembles a bell (hence the nickname). The bell curve is symmetrical. Half of the data will fall to the left of the mean; half will fall to the right.
Reflective ActivityThinking about your own class, draw a distribution graph showing distribution of pupil standards in PE 1.Does the shape of the graph change for just girls? 2.Does the shape of the graph change for just boys? 3.How might it look for other ‘groups’? EAL, FSM, Pupil Premium? Predict the effect on progress in classes where the teacher:
In the group discuss the potential impact on standards and progress |
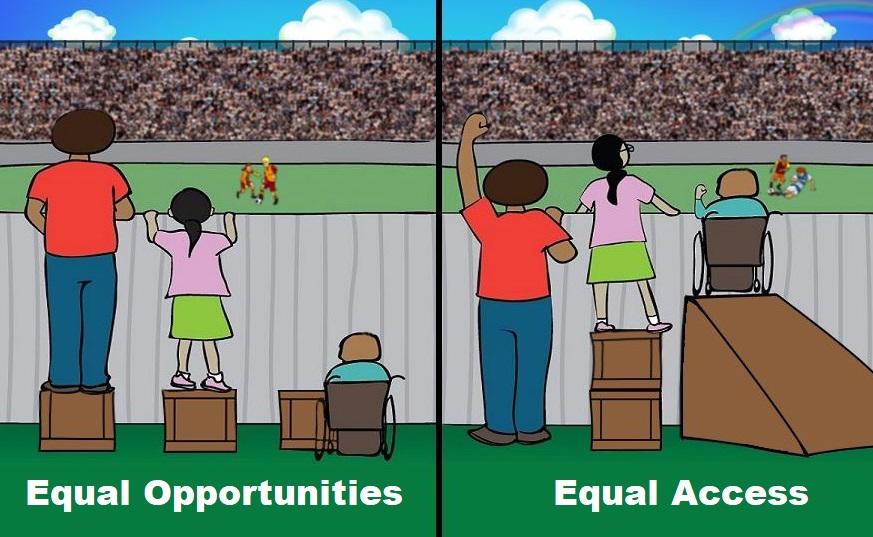
Reflective TaskConsider your own school.Are all children making good progress? If not, why not? Which groups of children are well served by the curriculum offer and which groups are poorly served by the PE provision? Identify the reasons why this might be the case. How we might gather evidence about pupils through observation. What are the opportunities to do this in a busy school day? |

