
Session 2
Assessment for learning and pupil progression.
Reflection ActivityRate yourself from 0 (not at all) to 5 (I do this consistently) Do you have confidence that every student in your class can improve? How well do you:
|
- An effective school is full of effective classrooms
- “It matters much less which school a child attends than which classrooms they are in at school.” (Wiliam 2007)
- Children fortunate enough to be in the most effective classrooms will learn in six months what students in an average classroom learn in a year
- In the least effective classrooms it will take two years
- What matters is the quality of the teaching

Key Messages about Assessment
- Removal of ‘levels’
- Prescription does not fit with freedoms
- Introduce own approaches to formative assessment
- Report as to whether on track to meet expectations at the end of a key stage
- Curriculum and assessment systems must meet the needs of your pupils
- Work with Subject Associations (and others) to produce a range of approaches
Assessment for Learning
Headline 1
- Re-emphasise the learning function of assessment
- De-emphasise the grading function
Assessment to improve learning or Assessment to prove learning?
What are summative and formative assessment?
The Garden analogy
Think of your students as flowers.
Summative assessment is to simply measure them. This might provide interesting data to be analysed and compared, but it does not effect how well they grow and develop.
Formative assessment is the process of watering and feeding the plants according to their needs – directly affecting their growth
Assessment is the insight we gather
Reflection ActivityCome up with a list of the MOST accurate and RELIABLE types of evidence that you might use to assess students in PE. What assessment methods do you currently use to provide evidence of attainment? You have 16 example of assessments in the table Please decide which are formative assessment and which are summative assessment |
|
Giving 5/10 for an end of topic test |
Completing your GCSE practical Assessment |
Watching a student complete a forward roll and giving them a tip for improving |
|
Observing a student's hurdling technique |
Awarding class members an end of KS3 level |
Deciding which theory set to put a student in |
|
Gaining an A* for the overall GCSE exam |
Using Year 8 end of year PE results to decide which pupils do GCSE and which B Tech |
Giving a PE merit certificate for achievement in a unit of work |
|
Testing whether pupils can swim a length for their 25m badge |
Telling student that they are level 5b for dance |
Timing and measuring for athletics badges |
|
Counting how many passes you can do in a minute to decide if you are ready to move on |
Seeing the score you can get in a sit and reach test |
Using a reciprocal task sheet to help another student learn a set shot |
|
Using thumbs up to see whether students have contributed to a problem solving task in OAA |
Judging how accurately John can hit his forehand drive |
Counting how many times weaker students hit the ball when batting |
Can you think of any other ways that you assess children’s progress in PE.. Is it summative or formative?
Assessment for Learning
Headline 2:
- Explore the relationship between curriculum and assessment for inclusive & progressive delivery
Reflection ActivityThe assessment practice for PE in your school.What is good, what not so good
|
Assessment for Learning
Headline 3:
- Use Assessment information to evolve your pedagogy. The better you communicate with learners the better their progress will be
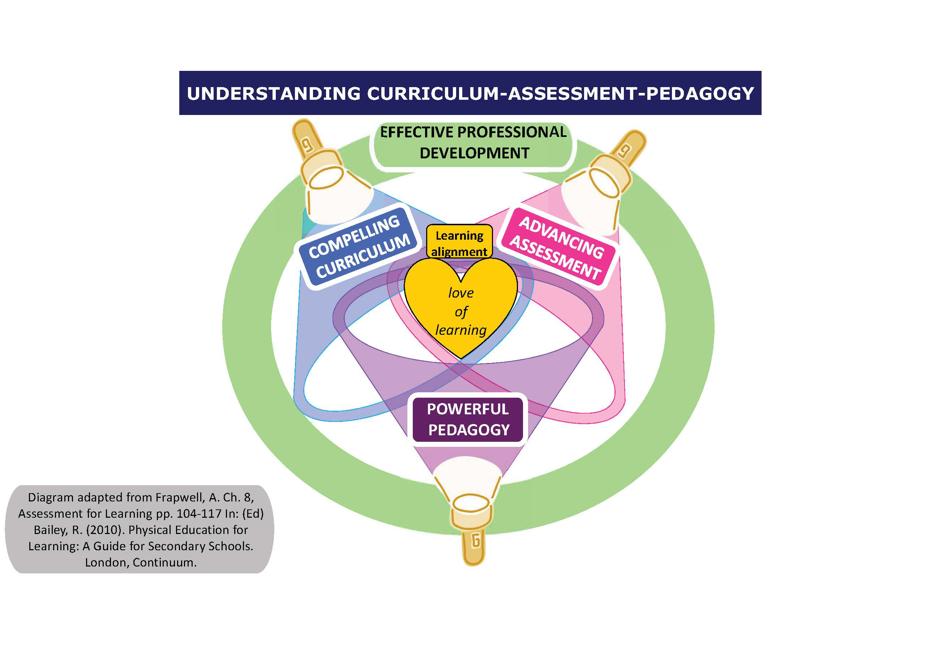
Reflection ActivityYou are about to teach PE to a Yr2 class of 30 children ( 16 girls,14 boys). At the end of Yr1 only 8 pupils could consistently catch a ball when thrown to them, the others could only catch when bounced to them. Very few could throw competently most tending to throw from a forward facing position. 2 pupils lacked the confidence to throw or catch any type of ball.
|
Assessment for Learning
Headline 4:
The Attainment target statutory has no level descriptors.
What and how we measure progress MUST change. Assessment HAS to be fit for purpose
The issues with levels
- Learning is not a linear process, so having a linear assessment protocol does not inform learning
- Level descriptors undermine learning
- The emphasis is on the grade rather than the learner
- Information about pupil attainment is misleading
- Parents have no clarity about how their children are performing in PE
Implications
Measure what we treasure / measure what we value
Rather than....
Attach a value to the measure
Types of Action
There are four types of action associated with assessment for learning and these are the communication tools that teachers need to constantly be seeking to improve:
- Eliciting information through questioning and dialogue.
- Providing feedback with emphasis on how to improve.
- Helping learners understand quality criteria.
- Peer- and self-assessment (which incorporates 1-3).
The Process of AfL
Establish a starting point
- based on what they have observed teachers will quickly come to a judgement about the ability of the pupils performing.
Negotiate a gap by setting targets
- Teachers will make decisions about what they want to improve in relation to the current performance of pupils and what they want to see pupils demonstrating.
Set strategies to improve
- Teachers will intervene and suggest ways of improving
ReflectionScenariosConsider the following scenarios that could happen in schools Consider how you might intervene to get the best outcomes for the pupils discussed. What AfL strategies could be deployed? |
|
Problem |
AfL strategies |
|
Max, Year 4, finds it difficult to stay on task in PE. He starts well but then loses focus mid- way through a task. He quickly loses heart and gives up. Then he mucks about. |
|
|
Josh, Year 6, District / Pro-club academy player, is keen to impress and do well, but his teacher’s feedback is usually along the lines of “Well done” or “Brilliant work, Josh. Keep it up!” |
|
|
Lisa, a year 5 pupil is approached by a visitor and is asked if she can tell them what she is learning in the lesson. Lisa is unsure and unable to answer. |
|
|
Janine, year 3, feels she never gets a chance to share her ideas or contribute within PE lessons. |
|
|
John, comes out of a PE lesson, he is heard overheard saying to a friend we have already done that in a science lesson. |
Reflection Activity |



AFL in Action – What I am looking for… (WILF)
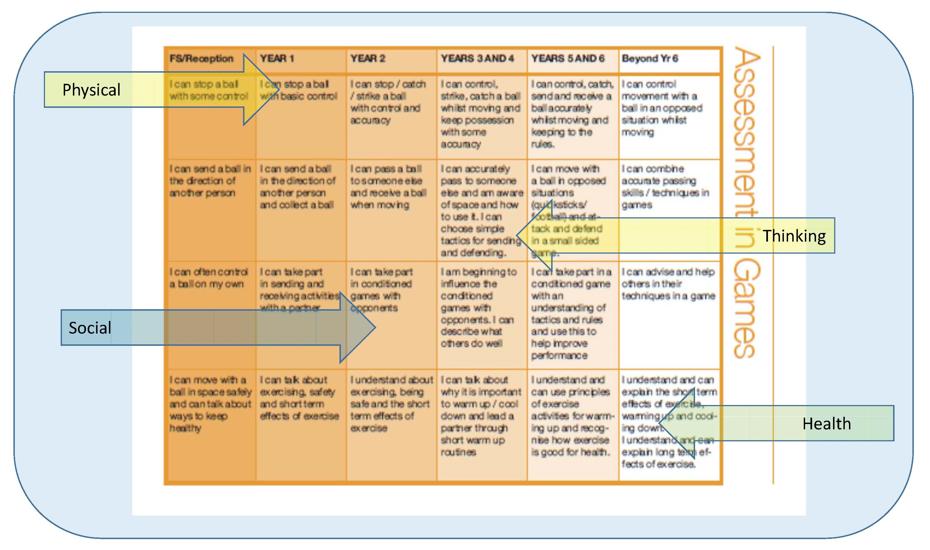
Reflection ActivityUsing the PE SOW assessment grids, identify and discuss ‘can-do’ or ‘WILF’ statements for each of the four domains. For the activities across one year of your Curriculum, tweak them to become ‘can-do’ statements for each unit. You must identify 2 statements for each domain for each block (8 in total) Ie .. 2 Thinking, 2 doing and 2 social, 2 Health. |
Summary
- The process of AfL relies on recognising a start point, detailing a target point and developing strategies with pupils to close the gap.
- The important thing to remember is that teachers are intervening, as a result of assessment information, to improve all pupils' performances.
- Assessment is at the heart of learning and teaching.
AfL is great but…
it is of no use if students do not act upon it.
- Feedback is the teacher identifying the next steps for progression or improvement.
- Feedforward is the action taken by the learners
Reflection Activity
|
Reflection ActivityWatch the lesson and identify where you see Assessment for Learning in action
Identify where you see children being engaged
|


