
Learning Episode One
The Importance of PE
Reflection ActivityPE memoriesConsider what your PE experiences as a learner. What were the positives/negatives? How could they influence your engagement as a teacher? |
The Importance of PE
Physical education plays a part in the lives of almost all children and young people’s education around the world. If the physical education experiences of those young people are to be positive and effective, then we need to know something about how it is taught, who is teaching it, what is being taught and how it can be improved.
In doing so, we can make a contribution to improvements in education, schooling, teaching and learning. Physical education can challenge and inspire. It can lead to life changes in terms of improved health, learning achievements and the development of positive relationships. While traditionally a subject in the curriculum our interests go beyond this to include extra-curricular activities associated with Physical Education such as field trips and sports clubs.
Researchers within the Physical Education Research Forum aim to engage in research that enhances our understanding of what effective teaching and learning is so that current policy, practice and professional development can be improved, challenged and even transformed.
Current policies in many countries around the world, views physical education in both primary and secondary schools as a logical site for the provision of opportunities for children and young people to be physically active. Furthermore, PE teachers are increasingly tasked with the responsibility to educate students about ways to lead a healthy and activity lifestyle. This logic is directly associated with global health concerns about the prevalence of chronic conditions such as cardiovascular disease and other major health risks related to sedentary lifestyle and obesity.
PE is associated with health and wellbeing, as a primary site for student engagement in the development of knowledge and understanding of issues related to health. Consequently, researchers within the Physical Education Research Forum aim to better understand this position for PE and what it means for teaching, learning and student experience. Importantly, group members also aim to challenge this position for PE, question the extent to which PE and PE teachers should be responsible for developing students’ physical health, and the extent to which current practice in PE can improve children and young people’s social, emotional and mental health.
- Physical Education is a compulsory part of the National Curriculum with programmes of study from KS1-4
- Pupils are statutorily entitled to Physical Education
Physical Education (PE) develops students' competence and confidence to take part in a range of physical activities that become a central part of their lives, both in and out of school. A high-quality PE curriculum enables all students to enjoy and succeed in many kinds of physical activity.
- Students who play sports are better able to concentrate and maintain focus, which has a positive impact on their academic life. This can lead to improved attainment in all other academic subjects.
- Regular exercise is vital in the fight against child obesity. We all know the many health problems that are associated with obesity and how important it is to lead a healthy, active lifestyle. Positive exercise habits that are implemented in childhood and adolescence will likely continue into adulthood.
- Students who exercise regularly have a better quality of sleep. They are therefore more alert at school and have higher levels of concentration.
- Physical exercise helps children relieve stress and anxiety. Young people today are arguably under more pressure than ever, so it is vital for them to have an outlet for this stress.
- Playing sports in groups help young people to improve their teamwork and leadership skills. It also helps to form stronger bonds between peers and promotes a healthy class dynamic.
- Physical activity promotes positive body image in teenagers, especially amongst women and girls. In this age of social media and societal pressure to look a certain way, this is of utmost importance.
- Sports teaches children to have improved self discipline. They can implement this self control in all aspects of their life, from better controlling their emotions to being more self motivated with their studies.
- PE helps children to develop their confidence. This can have a positive aspect on all areas of their life, such as their personal relationships and ability to integrate quickly and make friends, to thinking about their future goals.
- Sport helps children develop their motor skills and strengthen their muscles. When fine motor skills are developed, children will be more adept at handwriting or playing a musical instrument.
- Children who play regular sports have improved behaviour in school.
Reflective ActivityUnderstanding Terminology
Do they mean the same thing? Come up with working definitions of these key concepts noting the distinctions between them |

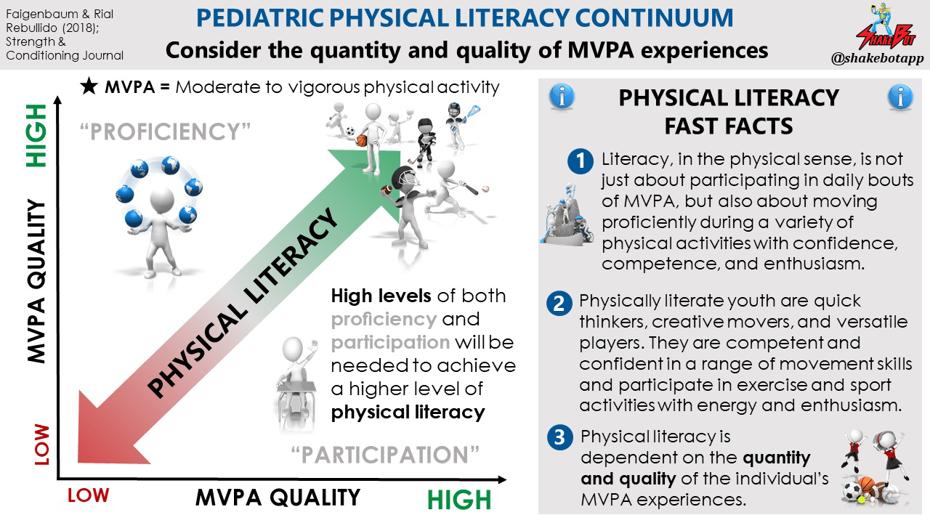
"Physical literacy is the motivation, confidence, physical competence, knowledge, and understanding to value and take responsibility for engagement in physical activities for life." - The International Physical Literacy Association, May 2014.
The following video explains it well
Reflective ActivityPhysical education, school sport and physical activity (PESSPA)What is Physical Education? What is School Sport? What is Physical Activity? Compare and contrast the PESSPA terms. Discuss their meaning giving examples of each in practice Develop a Venn diagram to illustrate similarities and differences of the terms. Demonstrate your understanding by listing examples in each of the sections created by the overlapping circles |
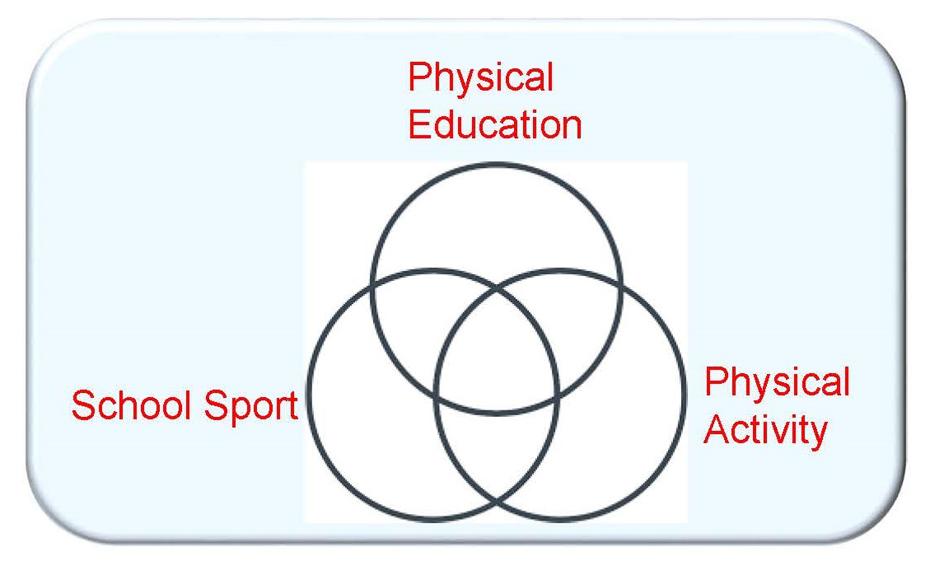
| Physical Education | School Sport |
Physical Literacy |
Physical Activity |
|
Broad educational benefits Inclusive of all ability levels Transferable learning Taught by qualified teachers Focus on learning through physical experiences |
Focus on skill development and performance Exclusive – most able and competitive succeed Associated with specialised learning Delivered by coaches Learning to be more physically skilful and tactically aware |
The foundation of PE and school sport The motivation, confidence, physical competence, knowledge and understanding to maintain physical activity throughout life Focus on the whole person Physical literacy is not a programme but an outcome |
Physical Activity is a broad term that describes bodily movement, posture and balance. It includes all forms of physical education, sports and dance activities. However, it is wider than this, as it also includes indoor and outdoor play, work-related activity, outdoor and adventurous activities, active travel |

